杂
Rethinking ImageNet Pre-training
Paper:Rethinking ImageNet Pre-training
code:-
Author:Kaiming He、 Ross Girshick 、Piotr Dollar 、Facebook AI Research (FAIR)
time:2018
Abstract
We report competitive results on object detection and instance segmentation on the COCO dataset using standard models trained from random initialization.The results are no worse than their ImageNet pre-training counterparts even when using the hyper-parameters of the baseline system (Mask R-CNN) that were optimized for fine -tuning pre-trained models, with the sole exception of increasing the number of training iterations so the randomly initialized models may converge.Training from random initialization is surprisingly robust; our results hold even when: (i) Using only 10% of the training data, (ii) for deeper and wider models, and (iii) for multiple tasks and metrics.Experiments show that ImageNet pre-training speeds up convergence early in training, but does not necessarily provide regularization or improve final target task accuracy.To push the envelope we demonstrate 50.9 AP on COCO object detection without using any external data–a result on par with the top COCO 2017 competition results that used ImageNet pre-training.These observations challenge the conventional wisdom of ImageNet pre-training for dependent tasks and we expect these discoveries will encourage people to rethink the current de facto paradigm of ‘ pre-training and fine -tuning’ in computer vision.
翻译:我们使用随机初始化训练的标准模型报告在COCO数据集上的物体检测和物体分割的竞争结果。即使使用baseline model的超参数,结果也不比它们的ImageNet预训练对应物差(Mask R-CNN)针对精细调整预训练模型进行了优化,唯一的例外是增加训练迭代次数,因此随机初始化模型可以收敛。随机初始化训练非常强大;我们的结果即使在以下情况下仍然存在:(i)仅使用10%的训练数据,(ii)用于更深和更宽的模型,以及(iii)用于多个任务和指标。实验表明在ImageNet预训练速度能加速训练时候的收敛速度,但不一定提供正则化或提高最终在目标任务上的准确性。为了突破这个范围,我们在不使用任何外部数据的情况下在COCO对象检测上达到了50.9 AP - 这个结果与2017年COCO相同使用ImageNet预训练的最好的竞赛结果差不多。这些结论挑战了ImageNet与训练对于依赖性任务的传统智慧,我们期望这些发现将鼓励人们重新思考计算机视觉中的“pre-training and fine-tuneing”范式。
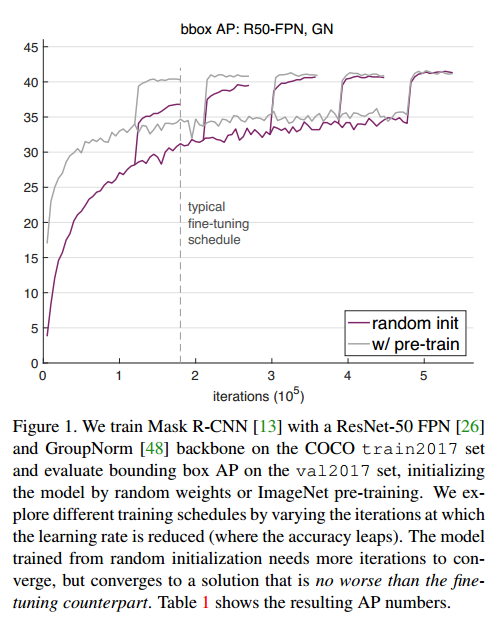
Contribution
- 采用基于ImageNet的预训练模型参数可以加快模型的收敛速度,尤其是在训练初期,而基于随机初始化网络结构参数训练模型时在采用合适的归一化方式且迭代足够多的次数后也能够达到相同的效果

采用基于ImageNet的预训练模型参数训练得到的模型泛化能力不如基于随机初始化网络结构训练得到的模型,前者更容易出现过拟合,因此需要选择合适的超参数训练模型,从而尽可能减少过拟合风险(前提是数据量足够大,比如10K以上的COCO数据集)
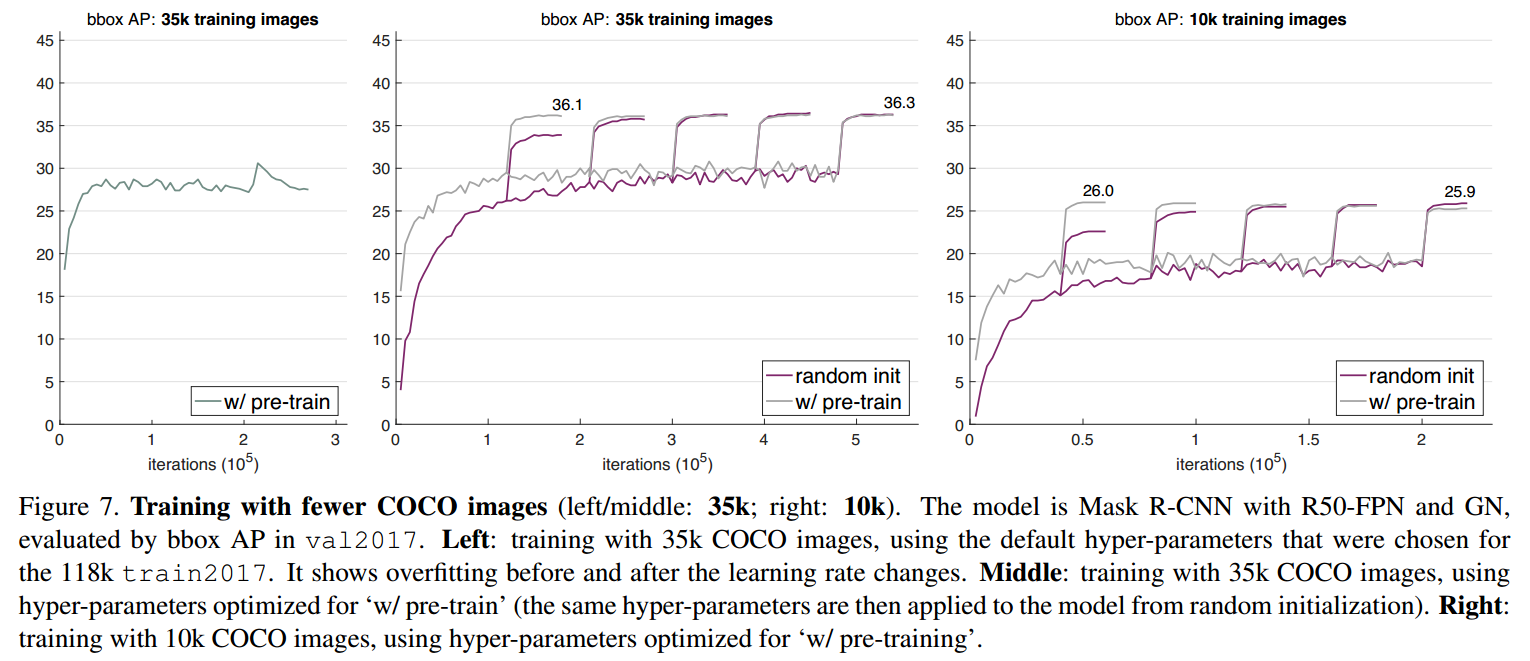
当迁移任务的目标对空间位置信息比较敏感时(比如目标检测、人体关键点检测任务),采用基于ImageNet的预训练模型并不会有太大的帮助
Summary
Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks
paper:Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks
code:-
Author:
time:2018
Abstract
Much of the recent progress made in image classification research can be credited to training procedure refinements, such as changes in data augmentations and optimization methods. In the literature, however, most refinements are either briefly mentioned as implementation details or only visible in source code. In this paper, we will examine a collection of such refinements and empirically evaluate their impact on the final model accuracy through ablation study. We will show that, by combining these refinements together, we are able to improve various CNN models significantly. For example,we raise ResNet-50’s top-1 validation accuracy from 75.3% to 79.29% on ImageNet. We will also demonstrate that improvement on image classification accuracy leads to better transfer learning performance in other application domains such as object detection and semantic segmentation.
翻译:近期图像分类领域取得的许多进展可以归功于训练过程的改进,比如图像增强的和优化方法的改进。然而在现在的文献中,大多数的改进要么是在实现细节中简单的提及,或者仅在源码中可见。在这篇论文中,我们将研究这些改进的方法,并通过消融研究凭经验评估它们对最终模型准确性的影响,我们将展示,通过将这些改进结合在一起,能够显著改进各种CNN模型,比如,我们在ImageNet上将ResNet-50的top-1验证集准确率从75.3%提高到79.29%。我们还将证明,图像分类准确率的提高可以在其他应用领域比如对象检测和语义分割中实现更好的迁移学习性能。
Contribution
Some tricks for training:
- Large-batch training
- Linear scaling learning rate
使用大的batch size,可能会减慢训练速度,对于收敛来说,收敛速度随着batch size的增加而变慢,换句话说,对于相同的迭代次数,用大的batch size比小的batch size 训练的模型验证集精度要低一些。He等人选择0.1作为batch_size=256时初始学习率,所以如果对于batch_size=b的,初始学习率可以选择0.1xb/256。 - Learning rate warmup
gradual warmup strategy:将学习率从0线性增加到初始学习率,比如,假设我们使用前m个batch的样本来预热,初始学习速率设为η ,那么在第i个batch的时候(0<=i<=m),学习率为iη /m。
- Linear scaling learning rate
- Low-precision
神经网络一般使用FP32(float point 32)训练,所有的数据都是以FP32格式存储,然而现在新的硬件可能对更低精度的数据类型增强了算术逻辑单元(也就是说,FP16要比FP32训练更快)尽管具有性能优势,但是精度降低后,范围更窄了,使得结果更可能超出范围,然后扰乱训练进度。建议存储所有参数和激活单元用FP16,并使用FP16计算梯度,同时,所有参数在FP32中都有一个副本用于参数更新,此外,将损失乘以一个标量可以更好的对齐使用FP16的梯度范围。 - Model tweaks
Model tweak是对网络体系结构的微小调整,例如改变特定卷积层的步长,这种调整通常几乎不会改变计算复杂性,但可能对模型的准确率具有不可忽略的影响。 - Trainging refinement
- Cosine learning rate decay
- Label smoothing
- Knowledge distilling
- Mix-up training
Summary
研究了十几个训练卷积神经网络的技巧,这些技巧包括对网络结构、数据预处理、损失函数和学习速率的调整,将所有这些堆叠在一起可以显著提高准确率。
Graph Neural Networks:A Review of Methods and Applications
paper:http://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.08434v1
code:-
Author:
time: 2018
Abstract
Lots of learning tasks require dealing with graph data which contains rich relation information among elements. Modeling physics system, learning molecular fingerprints, predicting protein interface, and classifying diseases require that a model to learn from graph inputs. In other domains such as learning from non structural data like texts and images, reasoning on extracted structures, like the dependency tree of sentences and the scene graph of images, is an important research topic which also needs graph reasoning models. Graph neural networks (GNNs) are connectionist models that capture the dependence of graphs via message passing between the nodes of graphs. Unlike standard neural networks, graph neural networks retain a state that can represent information from its neighborhood with an arbitrary depth. Although the primitive graph neural networks have been found difficult to train for a fixed point, recent advances in network architectures, optimization techniques, and parallel computation have enabled successful learning with them. In recent years, systems based on graph convolutional network (GCN) and gated graph neural network (GGNN) have demonstrated ground-breaking performance on many tasks mentioned above. In this survey, we provide a detailed review over existing graph neural network models, systematically categorize the applications, and propose four open problems for future research.
翻译:许多学习任务需要处理包含元素之间丰富关系的图形数据,比如物理系统建模、学习分子指纹、预测蛋白质界面和分类疾病需要一个模型来学习图形输入,在其他领域,如从文本和图像等非结构性数据中学习,对提取结构的推理,如句子的依赖树和图像的场景图,是一个重要的研究课题,也需要图形推理模型。图形神经网络(GNN)是连接模型,通过图形节点之间的消息传递捕获图形的依赖性,与标准神经网络不同,图形神经网络保留一种状态,该状态可以表示来自其邻域的任意深度的信息。虽然已发现原始图神经网络难以训练固定点,但网络架构,优化技术和并行计算的最新进展使得能够成功地学习它们。近年来,基于图卷积网络(GCN)和门控图神经网络(GGNN)的系统已经在上述许多任务中展示了突破性的性能。在本次调查中,我们对现有的图神经网络模型进行了详细的回顾,系统地对应用进行了分类,并为未来的研究提出了四个未解决的问题。
Contribution
Summary
Learning a Deep ConvNet for Multi-label Classification with Partial Labels
paper:hLearning a Deep ConvNet for Multi-label Classification with Partial …
code:-
Author:
time: 2019CVPR
Abstract
Deep ConvNets have shown great performance for single-label image classification (e.g. ImageNet), but it is necessary to move beyond the single-label classification task because pictures of everyday life are inherently multilabel. Multi-label classification is a more difficult task than single-label classification because both the input images and output label spaces are more complex. Furthermore, collecting clean multi-label annotations is more difficult to scale-up than single-label annotations. To reduce the annotation cost, we propose to train a model with partial labels i.e. only some labels are known per image. We first empirically compare different labeling strategies to show the potential for using partial labels on multi-label datasets. Then to learn with partial labels, we introduce a new classification loss that exploits the proportion of known labels per example. Our approach allows the use of the same training settings as when learning with all the annotations. We further explore several curriculum learning based strategies to predict missing labels. Experiments are performed on three large-scale multi-label datasets: MS COCO, NUS-WIDE and Open Images
翻译:深度卷积神经网络在单标签图像分类方面表现得非常好,但是有必要超越多标签分类任务,因为日常生活的图片本质上是多标签的。多标签分类比单标签分类更困难,因为输入图像和输出标签空间都更复杂。此外,收集干净的多标签标注比单标签标注更难扩展。为了减少标注成本,我们提出训练仅利用部分标签训练一个模型,即每个图像仅知道一些标签。我们首先根据经验比较不同的标记策略,以显示在多标签数据集上使用部分标签的可能性。然后为了学习部分标签,我们引入了一个新的分类损失,它利用了每个例子中已知标签的比例,我们的方法允许使用与学习所有注释时相同的训练参数设置,我们进一步探索了几种基于课程学习的策略来预测缺失标签实验。实验是在三个大型多标签数据集上进行:MS COCO,NUS-WIDE和Open Images
Contribution
- Empirically compare several labeling strategies for multi-label datasets to highlight the potential for learning with partial labels.
- Propose a scalable method to learn a ConvNet with partial labels.Introduce a loss function that generalizes the standard binary cross-entropy loss by exploiting label proportion information.
- A method to predict missing labels.
Summary
人脸识别
Git Loss for Deep Face Recognition
paper:Git Loss for Deep Face Recognition
code:https://github.com/kjanjua26/Git-Loss-For-Deep-Face-Recognition
Author:Alessandro Calefati, Muhammad Kamran Janjua, Shah Nawaz, Ignazio Gallo
time:2018
Abstract
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been widely used in computer vision tasks, such as face recognition and verification, and have achieved state-of-the-art results due to their ability to capture discriminative deep features. Conventionally, CNNs have been trained with softmax as supervision signal to penalize the classification loss. In order to further enhance discriminative capability of deep features, we introduce a joint supervision signal, Git loss, which leverages on softmax and center loss functions. The aim of our loss function is to minimize the intra-class variations as well as maximize the inter-class distances. Such minimization and maximization of deep features is considered ideal for face recognition task. We perform experiments on two popular face recognition benchmarks datasets and show that our proposed loss function achieves maximum separability between deep face features of different identities and achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on two major face recognition benchmark datasets: Labeled Faces in the Wild (LFW) and YouTube Faces (YTF). However, it should be noted that the major objective of Git loss is to achieve maximum separability between deep features of divergent identities. The code has also been made publicly available
翻译:卷积神经网络(CNN)已被广泛用于计算机视觉任务,例如人脸识别和验证,并且由于其捕获有辨别力的深层特征的能力而已经获得了最先进的结果。传统上,CNN已经用softmax作为监督信号进行训练以惩罚分类损失。为了进一步增强深度特征的判别能力,我们引入了一个联合监督信号Git loss,它利用softmax和center loss函数。我们的损失函数的目标是最小化类内距离以及最大化类间距离。这种深度特征的最小化和最大化被认为是面部识别任务的理想选择。我们在两个流行的人脸识别benchmark上进行实验,并表明我们提出的损失函数实现了不同身份的深面特征之间的最大可分离性,并在两个主要的人脸识别基准数据集上实现了最先进的准确度:LFW和YouTube Faces(YTF)。但是,应该指出的是,Git loss的主要目标是在不同身份的深层特征之间实现最大可分离性。该代码也已公开发布。
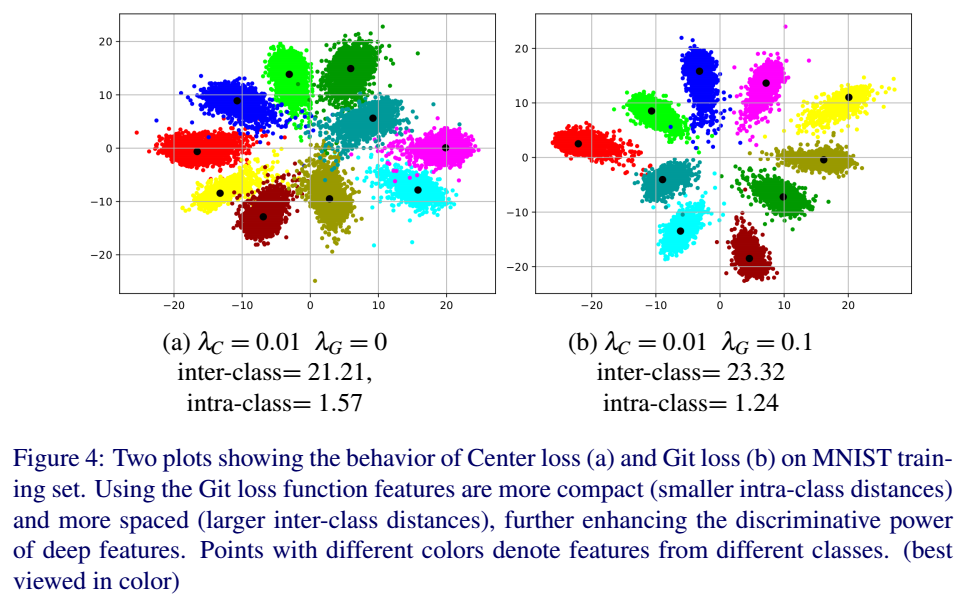
Contribution
- A novel loss function which leverages on softmax and center loss to provide segregative abilities to deep architectures and enhance the discrimination of deep features tofurther improve the face recognition task
- Easy implementation of the proposed loss function with standard CNN architectures.Our network is end-to-end trainable and can be directly optimized by fairly standard optimizers such as Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD).
- We validate our ideas and compare Git loss against different supervision signals. We evaluate the proposed loss function on available datasets, and demonstrate state-ofthe-art results.
Summary
在center loss的基础上增加了额外的约束,使学习到的特征比center loss具有更大的类间距离和更小的类内距离。
表情识别
Facial Expression Recognition with Inconsistently Annotated Datasets
paper:http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Jiabei_Zeng_Facial_Expression_Recognition_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf
code:https://github.com/dualplus/LTNet
Author: Jiabei Zeng, Shiguang Shan, and Xilin Chen
time: ECCV2018
Abstract
Annotation errors and bias are inevitable among different facial expression datasets due to the subjectiveness of annotating facial expressions. Ascribe to the inconsistent annotations, performance of existing facial expression recognition (FER) methods cannot keep improving when the training set is enlarged by merging multiple datasets. To address the inconsistency, we propose an Inconsistent Pseudo Annotations to Latent Truth(IPA2LT) framework to train a FER model from multiple inconsistently labeled datasets and large scale unlabeled data. In IPA2LT, we assign each sample more than one labels with human annotations or model predictions. Then, we propose an end-to-end LTNet with a scheme of discovering the latent truth from the inconsistent pseudo labels and the input face images. To our knowledge, IPA2LT serves as the first work to solve the training problem with inconsistently labeled FER datasets. Experiments on synthetic data validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in learning from inconsistent labels. We also conduct extensive experiments in FER and show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art and optional methods under a rigorous evaluation protocol involving 7 FER datasets
翻译:由于标注面部表情的主观性,标注错误和误差在不同的面部表情数据集种是不可避免的,归因于不一致的标注。当通过合并多个数据集扩大数据集时,现有的面部表情识别方法的性能不能持续提升,为了解决这种不一致性,我们提出了一种不一致的潜在真实伪标注(IPA2LT)框架,用于从多个不一致标记的数据集和大规模未标记数据中训练FER模型。在IPA2LT中,我们未每个样本分配多个带有人工标注或模型预测的标签,然后我们提出一种端到端的LTNet,其思想时从不一致的伪标签和输入的面部图像中发现潜在的真相(也就是真实标签)。据我们所知,IPA2LT是第一个用不一致标记的FER数据集来解决训练问题的工作,对合成数据的实验验证了所提出的方法从不一致标签中学习的有效性。我们还在FER中进行了大量实验,并表明我们的方法在涉及7个FER数据集的严格评估协议下优于其他最先进和可选的方法。
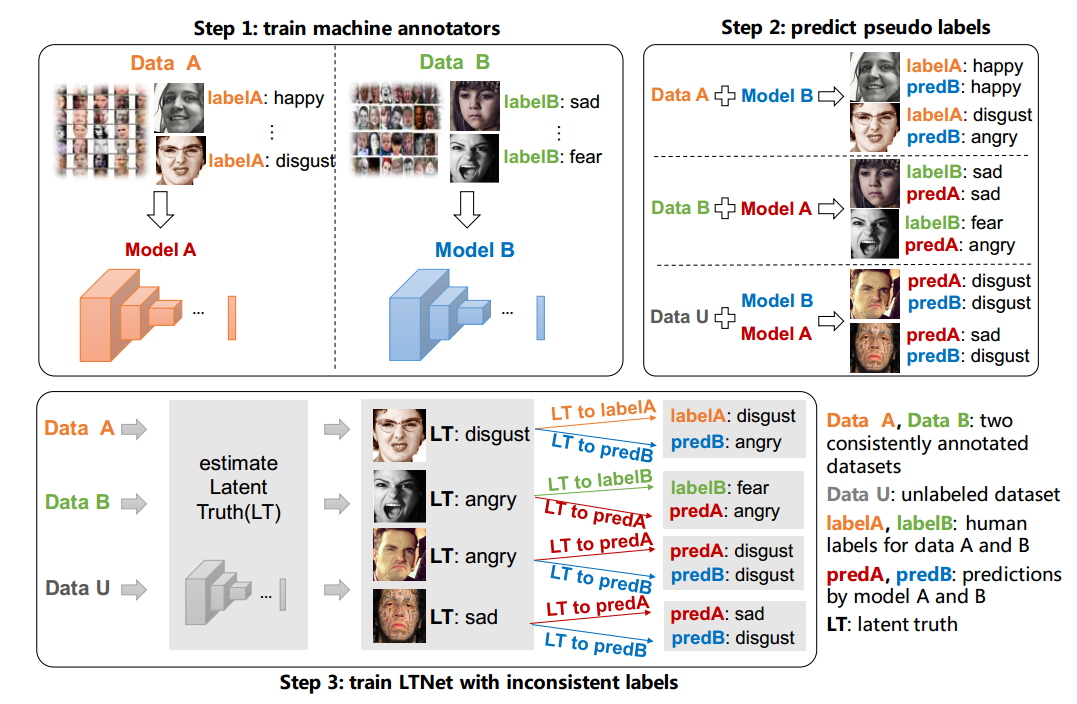
训练过程分为3步:
- 分别从数据集A和B中训练两个模型标注工具
- 模型的预测结果可能和人工标注不一致,它们将作为一些人工标注数据集和大规模未标注数据集中每个图片的多个标签,每个未标注数据作为数据集A和数据集B之间的桥梁,因为它们是用相同的模型预测出来的结果。
- 训练LTNet,预测图片输出隐藏的真实标签,
Contribution
- 提出了一个相对未研究过的问题:如何从多个标注不同的数据集中训练分类器,据我们所知,这是第一个解决不同的FER数据集标注不一致的工作
- 提出了IPA2LT的框架从多个标注不一致的数据集和大规模未标注的数据上训练一个FER模型,提出了一个端到端训练的LTNet
- 在合成数据和真实数据上的实验验证了所提出的方法在从不一致标签中学习的有效性,我们在FER中进行了广泛的实验,并在涉及7个FER数据集的严格评估写一下展示了IPA2LT优于现有技术的优势
Summary
从表情识别这一任务的特性–具有主观性,发现数据集标签不一致的情况,提出一个端到端的训练模型,从不一致的标签学习到标签之间潜在的关联,从而输出隐藏的真实标签,对于合并数据集来说,是一种方法,且有一定的合理性,并进行大量实验,发现在表情数据集上合并训练的效果要优于单独训练,并且本文提出的办法要优于其他混合的方法。
Facial Expression Recognition using Facial Landmark Detection and Feature Extraction on Neural Networks
paper:Facial Expression Recognition using Facial Landmark Detection and Feature Extraction on Neural Networks
code:
Author: Fuzail Khan
time: 2018.12
Abstract
The proposed framework in this paper has the primary objective of classifying the facial expression shown by a person using facial landmark detection and feature extraction. These classifiable expressions can be any one of the six universal emotions along with the neutral emotion. After initial facial detection, facial landmark detection and feature extraction are performed (where in the landmarks were determined to be the fiducial features: theeyebrows, eyes, nose and lips). This is primarily done using the Sobel horizontal edge detection method and the Shi Tomasi corner point detector. Thisleads to input feature vectors being formulated and trained into a Multi-LayerPerceptron (MLP) neural network in order to classify the expression beingdisplayed. Facial Expression Recognition (FER) is a significant step inreaching the eventual goal of artificial intelligence. If efficient methods can be brought about to automatically recognize these expressions, major advances may be achieved in computer vision.
翻译:本文提出的框架的主要目的是使用人脸关键点检测和特征提取对面部表情进行分类,这些可分类的表情可以是6种普遍情绪种的任何一种或者中性情绪,在初始的面部检测之后,执行面部关键点检测和特征提取,主要使用Sobel水平边缘检测方法和Shi Tomasi角点检测器完成。这导致输入特征向量被指定并训练成多层感知器(MLP)神经网络,以便对表情进行分类。FER是实现人工智能最终目标的重要一步,如果可以利用有效的方法自动识别这些表情,则可以在计算机视觉中实现重大进步。
Contribution
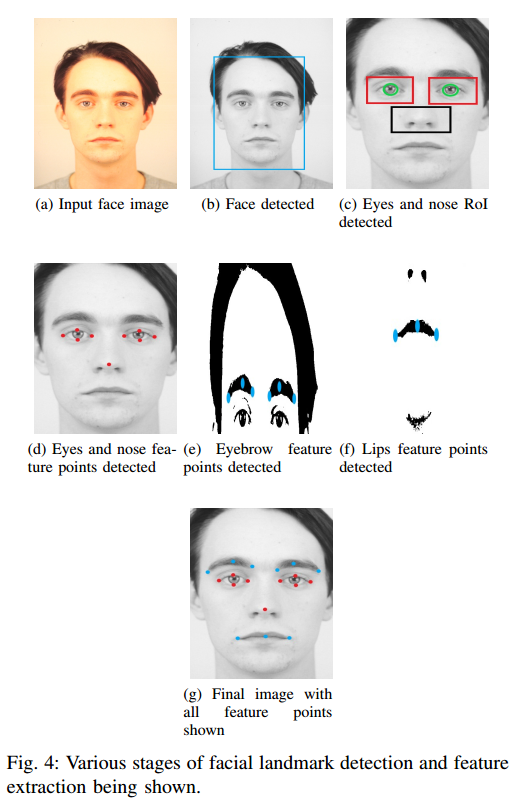
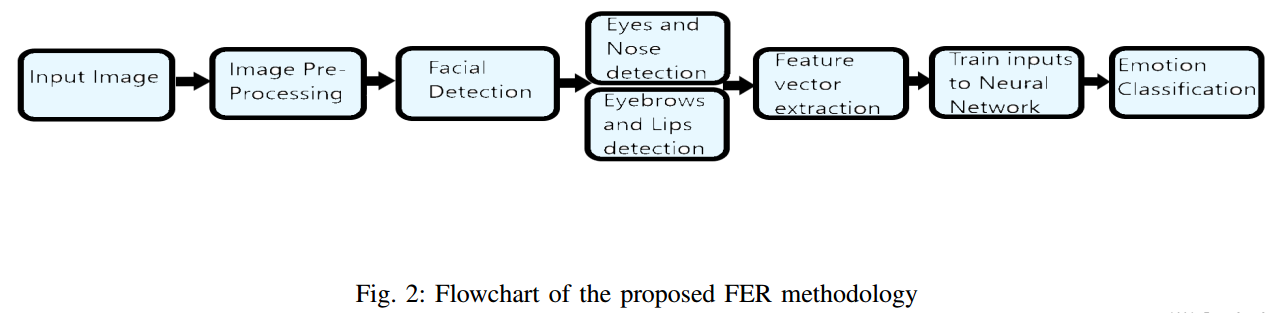
- 首先对输入的图片进行预处理,主要是去除不想要的噪声,增强图片的对比度,先用低通3x3高斯滤波器,有助于平滑图像并使梯度强度正则化,然后进行对比度自适应直方图均衡,用于光照强度修正
- 人脸检测利用基于Haar特征的级联分类器
- 关键点检测
- 人眼检测,主要是得到左眼和右眼的RoI,然后用于提取特征点
- 鼻子检测
- 眉毛和嘴唇检测
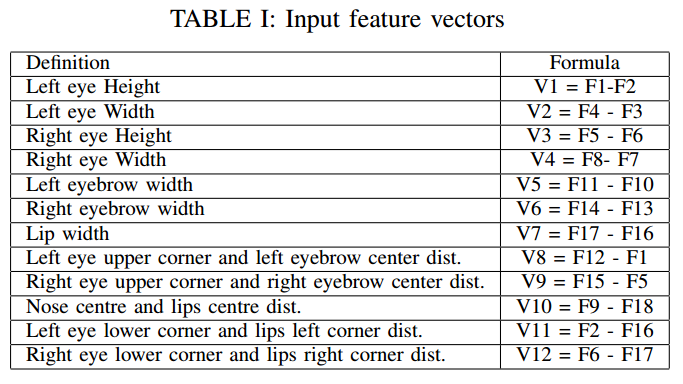
- 提取特征向量,通过上一步骤提取到了特征点(F1-F18),这一步使决定输入的特征向量送入神经网络中
- 训练神经网络,进行分类
Summary
这篇论文感觉方法还不是很先进,但是可能在某些特殊的数据集(表情很明显,图像质量比较好)效果会比较好,而论文选用的数据集从给出的例子来看,表情都是比较夸张的。
步态识别
GaitSet
paper:GaitSet:Regarding Gait as a Set for Cross-View Gait Recognition
code:https://github.com/AbnerHqC/GaitSet
Author: Chao, Hanqing and He, Yiwei and Zhang, Junping and Feng, Jianfeng
time: 2019
Abstract
As a unique biometric feature that can be recognized at a distance, gait has broad applications in crime prevention, forensic identification and social security. To portray a gait, existing gait recognition methods utilize either a gait template, where temporal information is hard to preserve, or a gait sequence, which must keep unnecessary sequential constraints and thus loses the flexibility of gait recognition. In this paper we present a novel perspective, where a gait is regarded as a set consisting of independent frames. We propose a new network named GaitSet to learn identity information from the set. Based on the set perspective, our method is immune to permutation of frames, and can naturally integrate frames from different videos which have been filmed under different scenarios, such as diverse viewing angles, different clothes/carrying conditions. Experiments show that under normal walking conditions, our single-model method achieves an average rank-1 accuracy of 95.0% on the CASIAB gait dataset and an 87.1% accuracy on the OU MVLP gait dataset. These results represent new state-of-the-art recognition accuracy. On various complex scenarios, our model exhibits a significant level of robustness. It achieves accuracies of 87.2% and 70.4% on CASIA-B under bag carrying and coat-wearing walking conditions, respectively. These outperform the existing best methods by a large margin. The method presented can also achieve a satisfactory accuracy with a small number of frames in a test sample, e.g., 82.5% on CASIAB with only 7 frames.
翻译:作为一种可以远距离识别的独特的生物识别特征,步态在预防犯罪、法医鉴定和社会安全方面具有广泛应用。为了描绘步态,现有的步态识别方法利用步态模板(其中时间信息难以保存)或步态序列,其必须保持不必要的顺序约束并因此丧失步态识别的灵活性,在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的视角,其中步态被视为由独立框架组成的集合。我们提出了一个名为GaitSet的新网络来学习集合中的身份信息。基于设定的视角,我们的方法不受帧的排列的影响,并且可以自然地整合来自在不同场景下拍摄地不同视频地帧,例如不同的视角,不同的衣服/着装。实验表明,在正常步行条件下,我们的单模型方法在CASIA-B步态数据集上实现了95%的平均Rank-1的准确率,在OU MVLP步态数据集上达到了87.1%的准确率。这些结果代表了新的最先进的步态识别准确率,在各种复杂场景中,我们的模型具有显著的鲁棒性,在携带包和穿着外套的行走场景中,CASIA-B的准确率分别达到了87.2%和70.4%的准确率,它们大大优于现有的最佳方法,本文提出的方法还在具有少量帧的测试样本下实现了令人满意的准确率,例如只有7帧的CASIA-B数据集达到了82.5%的准确率。
Contribution
Summary
神经网络和森林
Deep Neural Decision Forests
paper:Deep neural decision forests
code:
Author:
time:ICCV2015
Abstract
We present Deep Neural Decision Forests – a novel approach that unifies classification trees with the representation learning known from deep convolutional networks, by training them in an end-to-end manner. To combine these two worlds, we introduce a stochastic and differentiable decision tree model, which steers the representation learning usually conducted in the initial layers of a (deep) convolutional network. Our model differs from conventional deep networks because a decision forest provides the final predictions and it differs from conventional decision forests since we propose a principled, joint and global optimization of split and leaf node parameters. We show experimental results on benchmark machine learning datasets like MNIST and ImageNet and find onpar or superior results when compared to state-of-the-art deep models. Most remarkably, we obtain Top5-Errors of only 7.84%/6.38% on ImageNet validation data when integrating our forests in a single-crop, single/seven model GoogLeNet architecture, respectively. Thus, even without any form of training data set augmentation we are improving on the 6.67% error obtained by the best GoogLeNet architecture (7 models, 144 crops).
翻译:我们提出了深度神经决策森林–一个新的方法可以通过端到端的训练将分类树和深度卷积卷积网络中的表征学习功能统一起来。为了把这两个方法结合起来,我们引入了一个随机可微分的决策树模型,控制一般在(深度)卷积网络的初始层进行的表征学习。我们的模型不同于传统的深度网络,因为决策森林进行最后的预测,它与传统的决策森林不同,因为我们提出了分裂节点和叶子节点参数的联合全局优化原则。我们展示了在类似MNIST和ImageNet的benchmark上的实验结果,并与最先进的深度模型进行比较,发现了优于它们的结果。最值得注意的是,当我们在ImageNet验证数据上获得的Top5误差仅为7.84%/6.38%。因此即使没有任何形式的训练数据增强,我们也在最佳的GoogleNet架构(7种模型,144 crops)上得到6.67%的误差。
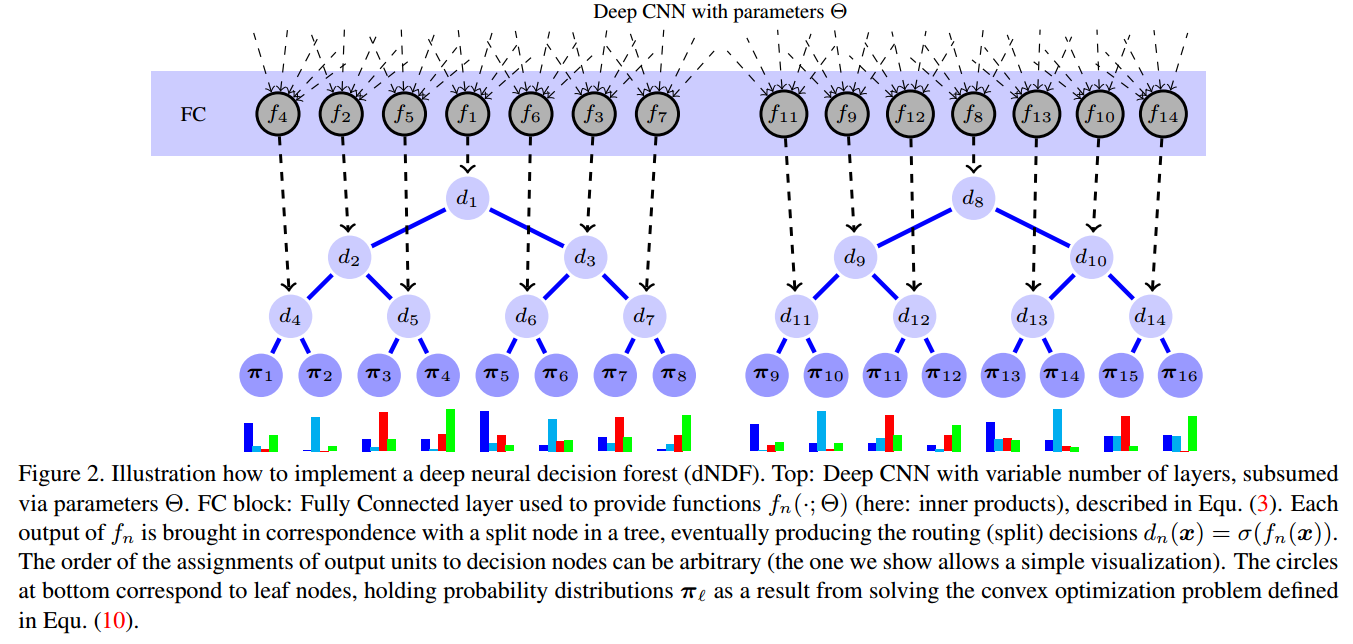
Contribution
论文提出将分类树模型和深度神经网络的特征学习相结合进行端到端训练的深度学习方法。该方法使用决策森林(decision forest)作为最终的预测模型,提出了一套完整的、联合的、全局的深度学习参数优化方法。在手写数据库MNIST和图像分类数据库ImageNet的实验中都取得了超越当前最好方法的结果。
Summary
和年龄估计的deep regression forest不同的是,这是针对分类任务的决策森林,DRF正是受这篇论文的启发,将分类转化为回归,这也是年龄任务的特点。
Distilling a Neural Network Into a Soft Decision Tree
paper:Distilling a neural network into a soft decision tree
code:
Author:Geoffrey Hinton 、Nicholas Frosst、Google Brain Team
time:2017
Abstract
Deep neural networks have proved to be a very effective way to perform classification tasks. They excel when the input data is high dimensional, the relationship between the input and the output is complicated, and the number of labeled training examples is large [Szegedy et al., 2015, Wu et al., 2016, Jozefowicz et al., 2016, Graves et al., 2013]. But it is hard to explain why a learned network makes a particular classification decision on a particular test case. This is due to their reliance on distributed hierarchical representations. If we could take the knowledge acquired by the neural net and express the same knowledge in a model that relies on hierarchical decisions instead, explaining a particular decision would be much easier. We describe a way of using a trained neural net to create a type of soft decision tree that generalizes better than one learned directly from the training data.
翻译:深度神经网络已经被证明是执行分类任务非常有效的方法,当输入数据是高维、输入和输出之间的关系很复杂、标记的训练样本数量很大时,表现优异。但很难解释为什么学习型网络会针对特定测试用例做出特定的分类觉得。这是因为它们依赖分布式层次表示(distributed hierarchical representations)。如果我们可以获取神经网络获得的知识并在依赖层级决策的模型中表现同样的知识,那么解释特定决策将更容易。我们描述了一种使用训练的神经网络来创建一种软决策树的方法,该决策树比直接从训练数据中学习有更强的泛化能力。
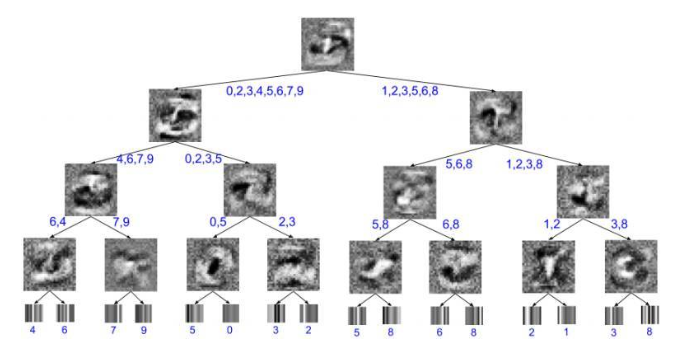
解释:上图为MNIST上训练的深度为4的软决策树的可视化图。内部节点处的图像是已学习的过滤器,而叶子处的图像是对已学习的类别概率分布的可视化。每片叶子最终最可能的分类,以及每个边缘的可能分类都被注释了。以最右边的内部节点为例,可以看到,在树的层级上,潜在的分类只有3或8,因此,学习的过滤器只是简单地学会区分这两个数字。其结果是一个查找连接3的末端的两个区域的过滤器,输出一个8。
Contribution
针对深度神经网络无法解释其具体决策的问题,提出软决策树(Soft decision tree),相较于从训练数据中直接学习的决策树,软决策树的泛化能力更强,并通过层级决策模型把DNN所习得的知识表达出来。
Summary
这篇论文和Deep neural decision forest不一样的是,这篇论文的重点是蒸馏(distillation),从DNN蒸馏出DT(decision tree),决策树去distilling 神经网络中的 knowledge,然后拿决策树去解释神经网络,而上一篇论文是将DNN和DT结合起来;上一篇论文是通过卷积神经网络得到原始数据的新特征放入决策树,本文是直接拿原始数据放入决策树。
Deep Neural Decision Trees
paper:Deep Neural Decision Trees
code:https://github.com/wOOL/DNDT
Author:Yongxin Yang, Irene Garcia Morillo, Timothy M. Hospedales
time:WHI 2018
Abstract
Deep neural networks have been proven powerful at processing perceptual data, such as images and audio. However for tabular data, tree-based models are more popular. A nice property of tree-based models is their natural interpretability. In this work, we present Deep Neural Decision Trees (DNDT) – tree models realised by neural networks. A DNDT is intrinsically interpretable, as it is a tree. Yet as it is also a neural network (NN), it can be easily implemented in NN toolkits, and trained with gradient descent rather than greedy splitting. We evaluate DNDT on several tabular datasets, verify its efficacy, and investigate similarities and differences between DNDT and vanilla decision trees. Interestingly, DNDT self-prunes at both split and feature-level.
翻译:已经证明了深度神经网络在处理感知数据(例如图像和音频)方面是强大的。但是对于表格数据,基于树的模型应用更多,基于树的模型的一个很好特性是它们的自然可解释性,在这项工作中,我们提出了深度神经决策树(DNDT)–通过神经网络实现的树模型网络。DNDT本质是可解释的,因为它是一棵树,然而,因为它也是一个神经网络,可以很容易地在NN toolkit中实现,并且使用梯度下降训练而不是贪婪地分裂。我们评估了几个DNDT地表格数据集,验证其功效,并研究DNDT之间地相似性和差异性,有趣地是,DNDT的分裂和特征级别地自我修剪。
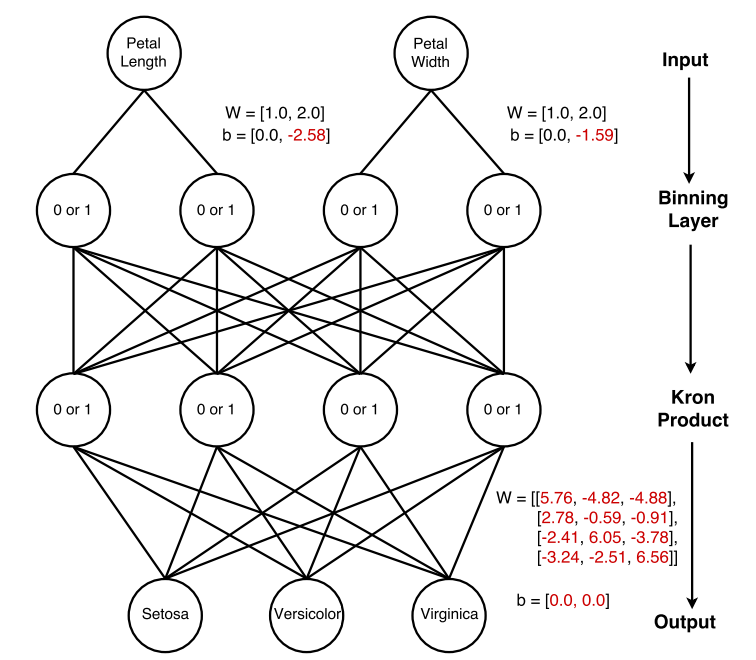
红色表示训练时的变量,黑色表示常量
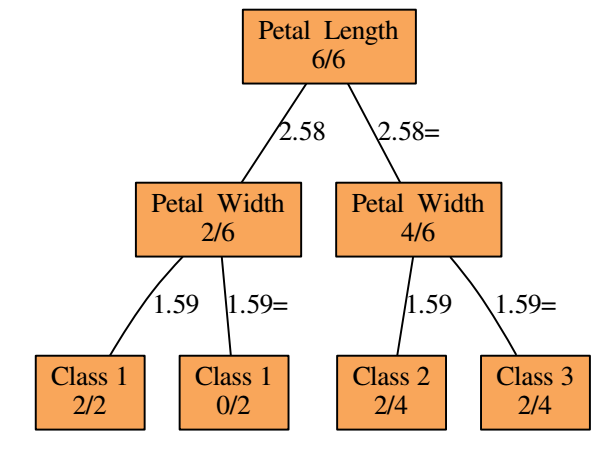
相同的网络用传统决策树展示,分数表示随机选择的6个事例的分类路线。
Contribution
Summary
和deep neural decision forest(Deep-NDF)不同的方面有:
- DNDT不是使用交替优化策略优化结构学习(splitting)和参数学习(score matrix),相反,直接使用反向传播来学习它们
- 不会将分割限制为二进制(左或右),因为我们应用可以将节点分成多个(>=2)叶子的可微分的bining functioin
- 我们专门为可解释性设计了我们的模型,特别是对表格数据的应用,我们可以解释每个输入特征,相比之下,NDF种的模型被设计用于预测性能并应用于原始图像数据,一些设计决策使它们不太适用于表格数据
模板
标题
paper:
code:
Author:
time:Abstract
翻译:
Contribution
Summary